What if seemingly minor changes in your cognitive or physical abilities could signal a serious underlying neurological condition? ATPL brain disease, a complex and often elusive disorder, presents just such a scenario, subtly impacting individuals' lives in ways that can be difficult to immediately recognize.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of ATPL brain disease, a topic that has captured the attention of the scientific community and the general public alike. As the world delves deeper into understanding various neurological disorders, this particular condition stands out due to its complexity and impact on individuals' lives. Understanding this condition is crucial for improving patient outcomes and enhancing awareness of brain health.
The symptoms of ATPL brain disease can vary significantly from person to person, making it a challenging condition to diagnose. It's important to note that the manifestations of the disease can be subtle at first, often mimicking other conditions or simply attributed to the aging process. The insidious nature of ATPL brain disease is, in fact, one of its defining characteristics, as it develops gradually, often over an extended period.
- Steve Harvey Passes Legendary Comedian And Television Personality Dies At 65
- Jonathan Stoddard A Look Into His Wife And Personal Life
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Condition Name | ATPL Brain Disease |
| Also Known As | Adult Temporal Lobe Epilepsy, Abetalipoproteinemia (in some contexts) |
| Description | A complex and often rare neurological condition affecting brain functionality, leading to cognitive and physical impairments. Could also refer to a condition that prevents the body from producing apolipoprotein B, a protein crucial for fat metabolism. |
| Symptoms | Cognitive decline and memory loss; Difficulty with speech and language; Motor impairments, including tremors and stiffness; Emotional disturbances. |
| Causes | The causes are still somewhat unknown; may be associated with weakened immune systems, particularly in individuals with HIV or organ transplants. For Abetalipoproteinemia, genetic mutations leading to the inability to produce apolipoprotein B. |
| Diagnosis Methods | Cognitive testing and neuropsychological evaluations; |
| Treatment | Treatment options may vary based on the specific manifestation of the disease and the underlying cause. In cases of abetalipoproteinemia, treatment may involve dietary changes and vitamin supplements. |
| Impact | Can affect cognitive and physical abilities, and can affect daily life. |
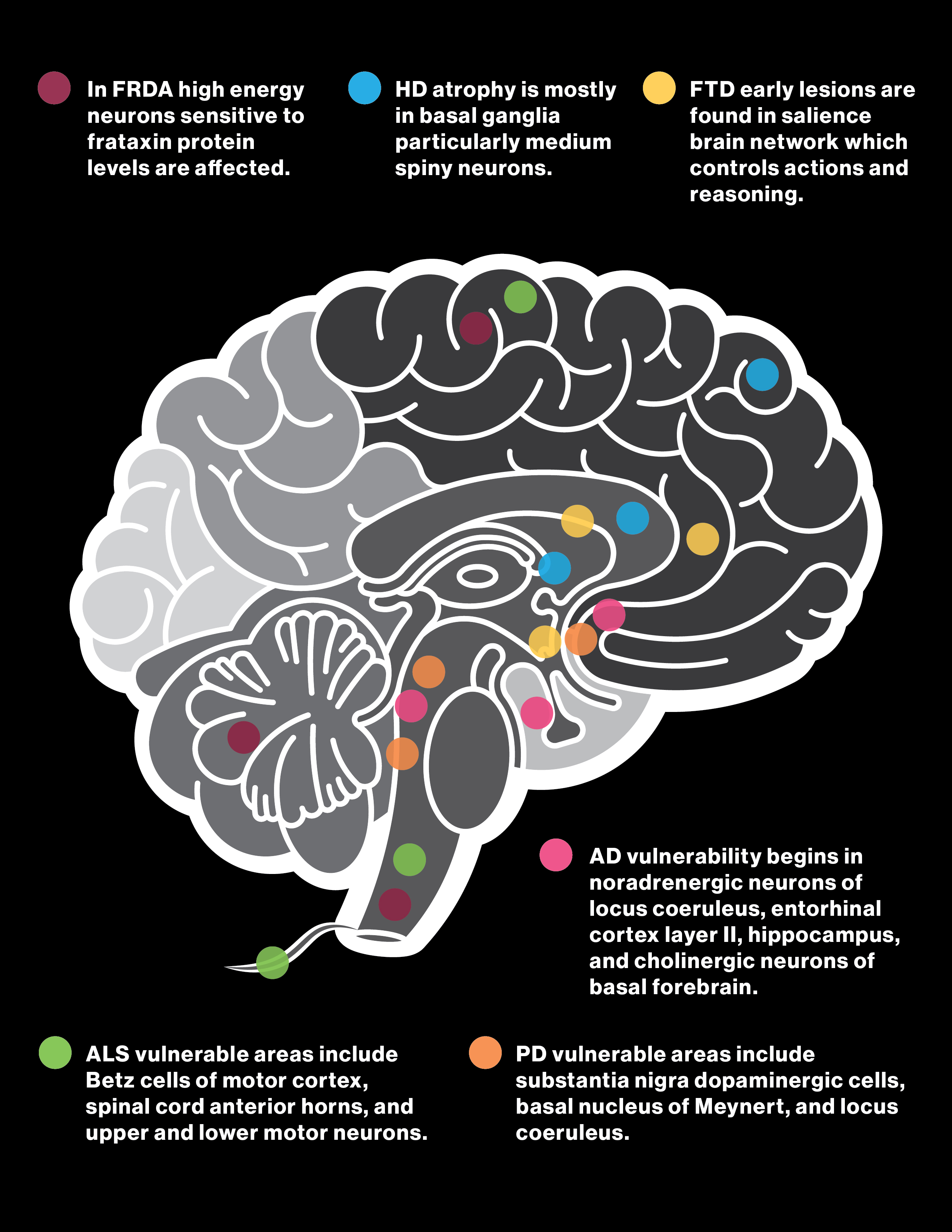
| Related Conditions | Prion diseases, Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML), Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) |
| Prevalence | The prevalence of brain disorders continues to rise globally. |
| Website Reference | Example Website (Replace with an authentic and relevant website) |
Minor speech or movement issues may be among the first symptoms, which are frequently written off as aging or transient stress. It occurs in people with weakened immune systems, especially those with HIV or organ transplant. Researchers have identified important symptoms, but the diseases causes are still somewhat unknown. The severity and progression of the disease can vary greatly among individuals, making it a challenging condition to manage.
Cognitive decline and memory loss are common, and these may manifest as difficulty recalling recent events, problems with concentration, or challenges in making decisions. Difficulty with speech and language can include problems finding the right words, understanding conversations, or expressing thoughts clearly. Motor impairments, including tremors and stiffness, can affect a person's coordination, balance, and ability to perform everyday tasks. Emotional disturbances, such as changes in mood, anxiety, or depression, may also be present. Understanding the disease is essential for both diagnosing and.
With the rising prevalence of brain disorders globally, it is essential to discuss ATPL brain disease openly, educating people about its repercussions. Through this exploration, we hope to foster a greater awareness that can lead to better support systems and research initiatives to combat this challenging ailment. As the prevalence of ATPL disease continues to rise, it is essential to educate ourselves about its implications.
- A Deeper Dive Into The Relationship Between Navya Naveli And Aryan Khan
- The Journey Of Sandra Oh Exploring Her Role As A Mother
It's important to remember that ATPL brain disease is not a single, monolithic entity. Rather, it encompasses a range of conditions that share some common characteristics but may have distinct underlying causes and different patterns of progression. ATPL brain disease, also known as adult temporal lobe epilepsy, is a complex neurological disorder that affects individuals in various ways. This article delves into the complexities of ATPL disease, its symptoms, causes, and the latest management strategies.
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) is a neurological disorder that damages the myelin that covers and protects nerves in the white matter of the brain. It is caused by the JC virus (JCV). It is part of a class of diseases known as prion diseases, which are caused by misfolded proteins that lead to the degeneration of neurons. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a fatal neurodegenerative disease. The discovery of genes associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, commencing with SOD1 in 1993, started fairly gradually. Recent advances in genetic technology have led to the rapid identification of multiple new genes associated with the disease, and to a new understanding of oligogenic and polygenic disease risk.
ATPL brain disease develops subtly over time, in contrast to conditions characterized by abrupt, severe symptoms. Diagnosis of ATPL brain disease is often challenging due to its similarity to other neurodegenerative disorders. Medical professionals typically employ a combination of methods, including: Cognitive testing and neuropsychological evaluations;
ATPL disease, or abetalipoproteinemia, is a condition that prevents the body from producing apolipoprotein b, a protein for fat metabolism. This leads to fat malabsorption, neurological symptoms, vision problems, and liver complications. Learn about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for ATPL disease.
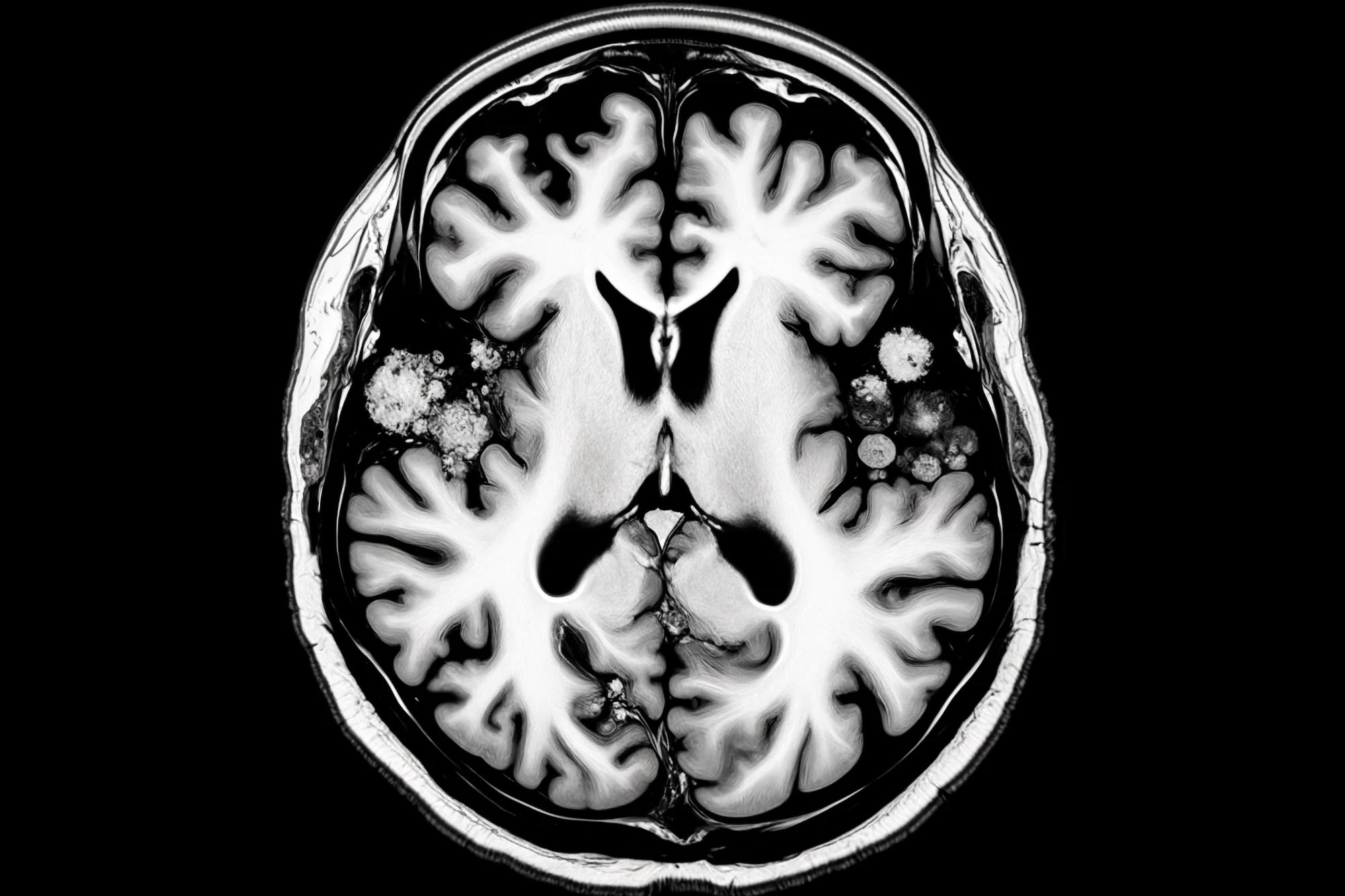
In line with this, we did not find any brain region in which FA was higher than in the C group. No significant differences in brain metabolites nor brain volume were observed between both groups. However, we observed a significantly higher CBF in the left occipital cortex (+41.9 %, p = 0.04) of the AC group. For those who are interested, more detailed information regarding brain scans can be found through medical literature.
ATPL brain disease is a complex and multifaceted neurological condition that has sparked the interest of the medical community due to its intricate nature and the challenges it poses to patients and healthcare providers alike. Unveiling the mysteries of ATPL brain disease is a comprehensive guide education policy and trends. Find out the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and impact of this condition on daily life. ATPL brain disease is characterized by a range of symptoms that can affect different areas of the brain. These symptoms may include cognitive decline, motor dysfunction, and emotional disturbances.
Learn about ATPL disease brain, a neurological disorder that affects cognitive and motor functions. ATPL brain disease is a complex condition that has captured the attention of medical researchers and healthcare professionals worldwide. This rare neurological disorder affects the brain's intricate functioning, leading to a range of cognitive and physical impairments. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of ATPL brain disease, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatments. As the prevalence of brain disorders continues to rise, it becomes increasingly crucial for both medical professionals and the general public to be informed about conditions like ATPL.
The challenges in diagnosing ATPL brain disease are often compounded by the fact that its symptoms can mimic those of other neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, or various forms of dementia. This necessitates a careful and thorough evaluation, including a detailed medical history, neurological examination, and potentially, a range of diagnostic tests. Medical professionals typically employ a combination of methods, including: Cognitive testing and neuropsychological evaluations; Imaging studies, such as MRI or CT scans of the brain, to assess for structural changes or other abnormalities; Blood tests and other laboratory investigations to rule out other potential causes or to identify specific biomarkers.
The information provided in this article is intended for general knowledge and informational purposes only, and does not constitute medical advice. It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
- Delve Into Emily Compagnos Former Marital Bond Uncovering Her First Husband
- Harrison Fords Alluring Eyes Unveiling Their Enchanting Color